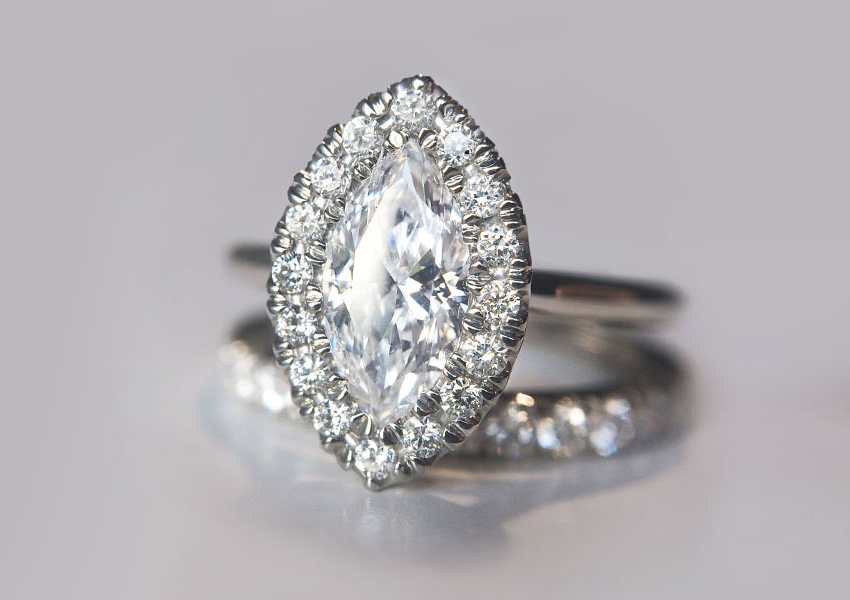

Mined Diamonds
Timeless, elegant and classic. We’ve made diamonds our obsession!
Mined Diamonds
Timeless, elegant and classic. We’ve made diamonds our obsession!






Why Mined Diamonds?
They're timeless
With their neutral colour and long tradition you could argue that diamonds will never go out of style! They are also incredibly versatile and they work with a wide and exciting range of designs making them the perfect gemstone to suit every taste.
Value
Diamonds aren’t cheap but this is often the very reason they are chosen to mark life’s most valuable love stories.
Hardness
Who said being practical isn’t romantic? Diamonds are the hardest known mineral, meaning that they are resistant to the scratches that can make other gemstones appear dull and lifeless with wear. Along with Sapphires and Rubies (which are the next hardest gemstones) diamonds are a fantastic option for an engagement ring if you intend to wear it every day.
Beauty
Last but certainly not least – they are beautiful! A well cut diamond will create the perfect balance between fire and sparkle, diamonds give life to a piece and there’s no wonder they
About Diamonds
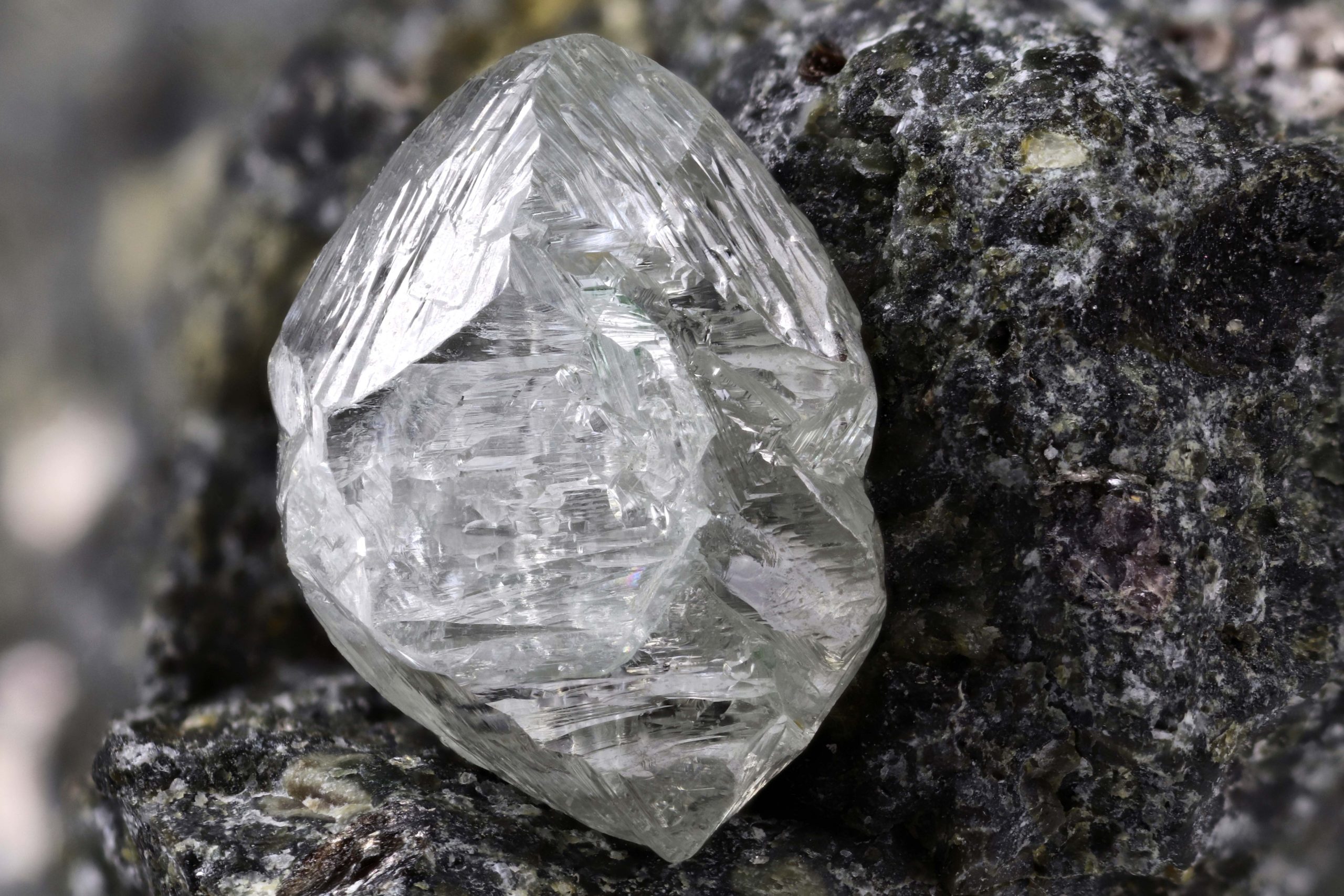
Where do diamonds come from?
Diamonds are formed in the upper mantle of the Earth in an environment of high pressure and high temperature. It is unknown how long they took form, with estimates anywhere from days and weeks to millions of years. Deep volcanic eruptions resulted in molten rock speeding toward the Earth’s surface, forming pipes of mineral rich igneous rock – now known as Kimberlite
Diamonds are then accessed through digging into the earth (mining) or by filtering alluvial deposits such as riverbeds
Very brief history of diamonds in jewellery
According to the GIA, some historians have estimated that India was trading in diamonds as early as the fourth century BC. In the early 1700 the supply in India began to decline and diamonds began to be discovered in Brazil, which dominated the diamond market for the next 150 years. By the 1800s European and American explorers discovered huge diamond deposits in South Africa, though still rare, these new discoveries meant that diamonds were no longer the exclusive riches of the royal and noble. From 1947 diamonds became synonymous with engagement rings following the most famously successful marketing campaign by DeBeers, coining the phrase ‘Diamonds are forever’. Diamonds have continued to be discovered across the world in countries including Russia, Australia and Canada.
The ethics of diamonds
In their history, diamonds have been involved in devastating human rights violations, some of which were infamously depicted in the 2006 film Blood Diamond. Since 2003 conflict free diamonds have been available through the Kimberley Process Certification System and World Diamond Council’s System of Warranties, both of which are explained in more detail here.
The future of diamonds is continually evolving with the availability of fully traceable Canadian Diamonds and more recently Everledger’s Blockchain traced diamonds.
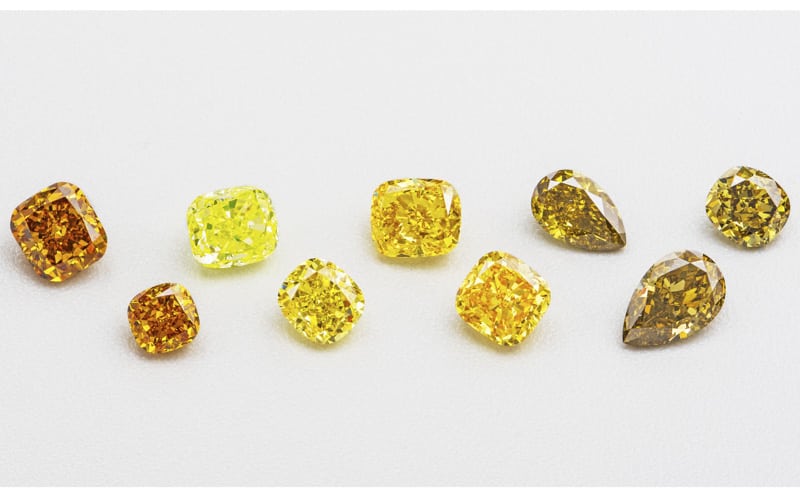


Coloured Diamonds
About Coloured Diamonds
Observed in virtually every colour of the rainbow, coloured diamonds are a result of various different elements being present at the time the diamond was formed. Coloured diamonds are significantly rarer than diamonds in the D-Z colour range, and as such, they can command some of the highest prices of diamonds sold. Nicknamed ‘Fancy Diamonds’, rare coloured diamonds can truly make your forever piece stand out from the crowd.
Hue, Tone and Saturation
The body colour is graded by looking at hue, tone and saturation. Hue is your first impression of the stone (noting the appearance of red, blue, green or anything in between). Tone refers to the lightness and darkness of the colour. Saturation is a colour’s strength or intensity, for example if a blue diamond is high in saturation it could have quite a rich blue colour. The GIA explains the magic of coloured diamonds, breaking down which elements cause each colour as well as the quality factors to consider when selecting your perfect coloured diamond.
Live Loose Diamond Search
Find a diamond
Shape

Carat Weight
Cut
Colour
Clarity
Type
Select the perfect diamond shape for you. Round Brilliant diamonds are undoubtedly the most popular for their fire and sparkle but if you are looking for the variety and character of a fancy shape then see what else is available.
The size that suits your design, your taste and your budget. Carat weight refers to how heavy a diamond is. It is indicator of the size of the diamonds, however, you should refer to the measurements of the stone to get like for like comparisons.
The quality of a diamonds is arguably all about cut. An Excellent cut diamond will be fashioned so that it’s proportions, symmetry and polish result in superb brilliance, fire and sparkle.
White diamonds are graded by how colourless they are in appearance. D-F are Colourless, G-I are Near Colourless and K-Z are Tinted. The difference between each colour grading is slight and saving on colour can free up spending on the other Four Cs.
Clarity is an assessment of the number and position of visible inclusions in a diamond. For some shapes such as Emerald cut diamonds clarity is key, while for other more brilliant cuts, inclusions can become less noticeable.
Clarity is graded using the following abbreviations: IF/F meaning Internally flawless/ Flawless, VVS meaning Very Very Slightly included, VS meaning very slightly included, SI meaning Slightly Included and I is Included.
Polish grading is a recognition of how finely a diamond cut was finished. A diamonds Polish should enhance the cut by not interfering with light return.
Diamonds cuts are carefully calculated and planned for optimum light performance and beauty. The facets in a diamond should be perfectly aligned and shaped.
The depth of a diamond will impact the light performance and appearance of size. If a diamond is deep a lot of it’s carat weight will be ‘hidden’ beneath the stone where it can’t be enjoyed and the diamond will look smaller. Depth of a diamond also impacts light performance and a diamond that is too deep or too shallow will leak light.
The table needs to be well balanced to the proportions of the diamond. For a Round Brilliant diamond, the table should be around 54% – 57%
Fluorescence is the phenomenon in a diamond that causes a stone to produce a colour reaction (usually blue) in response to ultraviolet light. ‘Strong fluorescence’ is generally avoided as it can make a diamond appear hazy, however in some instances, faint blue fluorescence can improve the appearance of a diamond with low colour, in making it look whiter in daylight.
Our diamonds above 0.30ct will come with certification from an independent, reputable diamond grading laboratory. These include The American Gem Society (AGC), the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the International Gemological Institute (IGI)
Choose any special criteria for your diamond; Crafted by Infinity (CBI) for their impeccable cut quality, Mined diamonds from the Earth, Canadian diamonds with guaranteed provenance, or Lab Grown diamonds taking advantage of cutting edge technological developments.
Length-Width ratio of a fancy shaped diamond can be a matter what suits your personal taste and the ring design but it can also impact the beauty of the stone. Ideal ratios for different fancy shaped diamonds include Emerald diamonds = 1.34 – 1.43, Oval diamonds = 1.35 – 1.45, Pear diamonds = 1.47-1.65 and Marquise diamonds = 1.90 – 2.10
AS SEEN IN






























