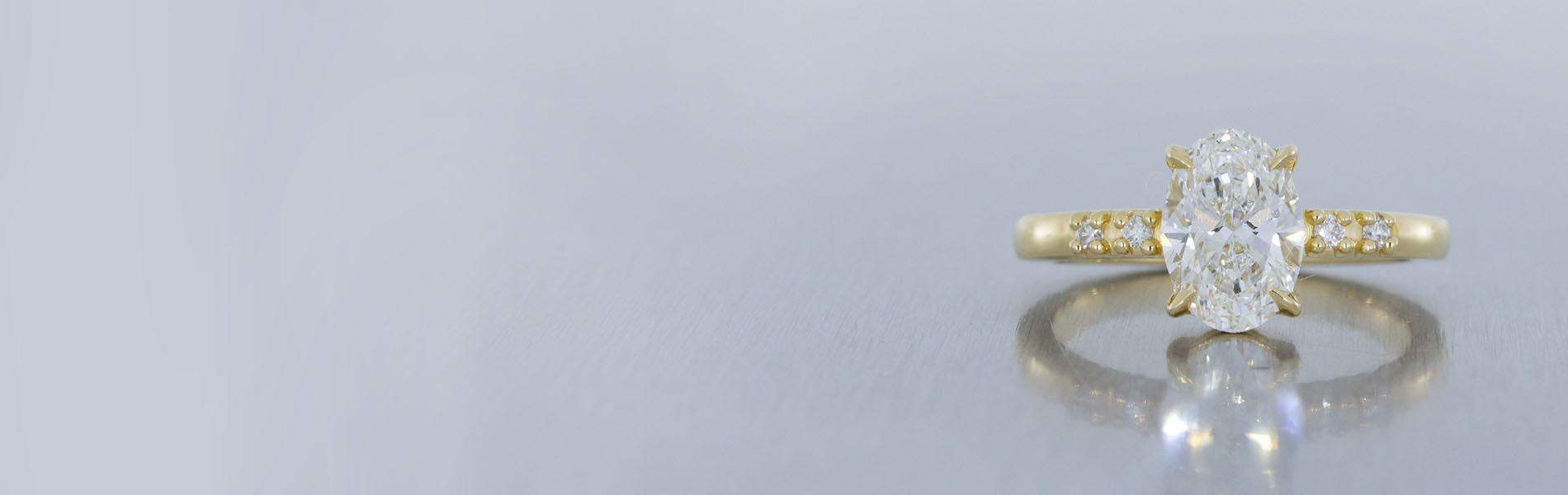

Lab Grown Diamonds
“Mined diamonds are a gift of nature whereas man-made diamonds are a gift of human wisdom.”
Lab Grown Diamonds
“Mined diamonds are a gift of nature whereas man-made diamonds are a gift of human wisdom.” *
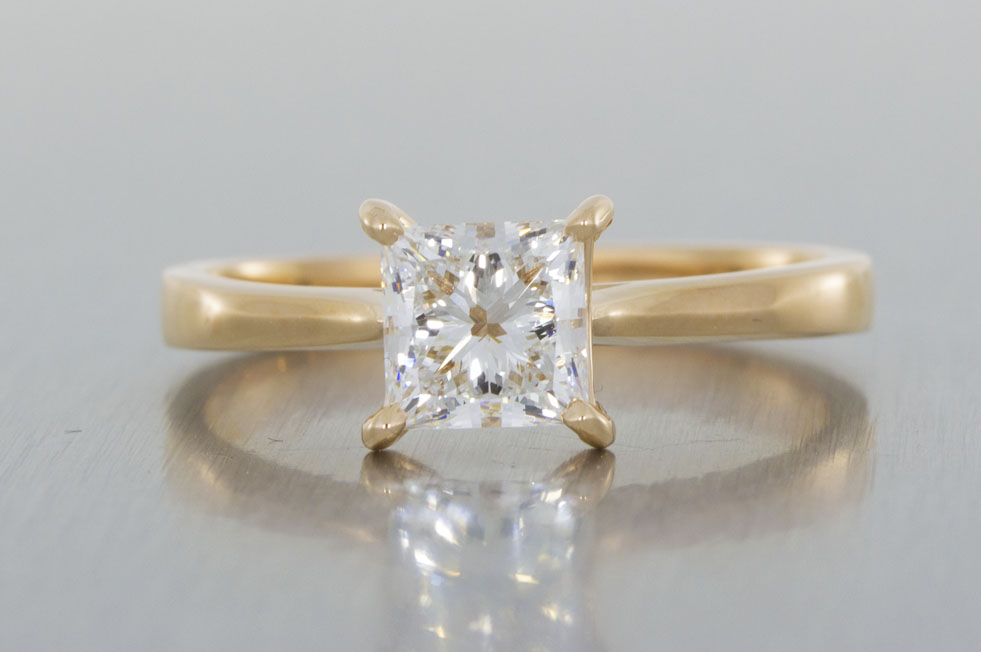






Why Lab Grown Diamonds?
Value
You can expect to pay around 30% less for a lab grown diamond compared to a mined diamond, the price difference could allow you to upgrade to a larger or clearer diamond. Lab grown diamonds do not involve the same long supply chains and mining expenses of mined diamonds. They are also not a finite resource and it is possible to produce lab grown diamonds to order.
Alternative to Mined Diamonds
Grown in controlled laboratories, lab grown diamonds do not involve the mass land displacement and ecological harm associated with open pit mining or deep-sea dredging. Even the most responsible forms of diamond mining have an ecological impact (some diamond mines are now visible from space.)
Using machines and highly skilled workers to operate and develop the technology needed to create lab grown diamonds eliminates the risk of human exploitation. Furthermore, coming from such controlled environments means lab grown diamonds are completely conflict free.
Though lab grown diamonds are by no means cheap, their affordability means that more people have access to owning and creating diamond jewellery to be loved for generations, at a lower initial investment.
About Lab Grown diamonds
Lab Grown diamonds are real diamonds!
Lab grown diamonds are real diamonds as classified by the US Federal Trade Commission.
Lab grown diamonds are chemically, optically and physically identical to mined diamond and should not be confused with Diamond Simulants such as Cubic Zirconia and Moissanite which are chemically different to mined diamonds.
The important difference you need to know about lab grown diamonds is their origin
Mined diamonds were created in the intense heat and pressure of the Earth’s mantle a few billion years ago. Volcanic activity brings them closer to the earth surface where they can be mined. Lab grown diamonds are also created in intense heat and pressure, but this time above ground under a highly controlled environment.
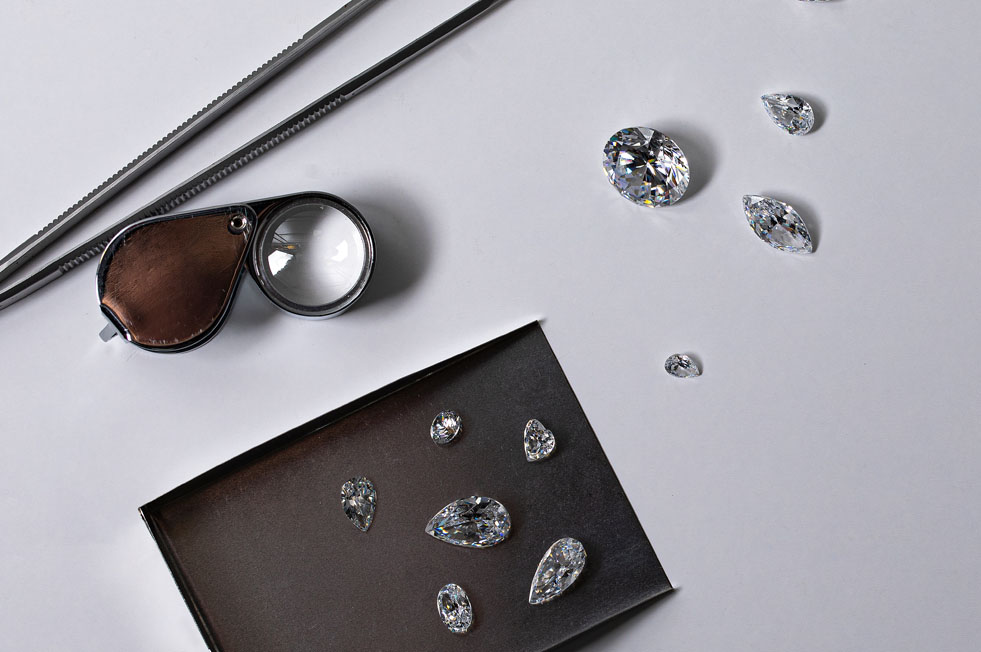


How Are Lab Grown diamonds Made?
High Pressure High Temperature
High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) expertly replicates the natural conditions of the Earth’s mantle where mined diamonds were formed.
Carbon, along with a diamond seed, is placed into a cell under temperatures up to 1500C and immense pressure, which dissolves the carbon into gas. (The GIA compares this to the pressure you would experience if you balanced a jumbo jet on the tip of your finger.) (directly lifted from HPD can we get permission to copy it?). The loose carbon then condenses onto the diamond seed, using the seed as a template and following the isometric crystal structure of a diamond.
Once the newly formed diamond is harvested, it is cut, polished and graded in the same way as a mined diamond.
Chemical Vapor Deposition
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) provokes controlled chemical reactions, creating a carbon rich ‘rain’, which, in the unique conditions of a CVD growth chamber, builds layer by layer into a diamond.
In low pressure and high temperature conditions, carbon rich gases (hydrogen and methane) are converted into the ingredients and chemical conditions needed for a diamond to grow. As the gasses fall down to the base of the chamber, carbon atoms attach themselves layer by layer to a diamond seed, following the isometric crystal structure of a diamond and slowly forming a diamond.
Once the newly formed diamond is harvested, it is cut, polished and graded in the same way as a mined diamond.
History
The first lab grown diamonds were created in the 1950s. The two techniques, CVD in 1954 and HPHT in 1956 were developed in parallel.
The unrefined ancestors of the modern lab grown diamond were too small and too saturated in colour to be used in jewellery.
It wasn’t until the 1980s that the technology was refined and gem quality lab grown diamonds were a possibility, and even more recently in the 2010s that lab grown diamonds could truly compete with their mined counterparts, being made into fine jewellery.
Lab grown diamond technology is continuously evolving and the popularity of lab grown diamonds is increasing year on year by between 15% – 20%
What do I need to know about lab grown diamonds
Future Value
You’re probably looking to create an engagement ring as a symbol love and commitment, not with the intention of selling it down the line but future value is understandably something you are considering. As lab grown diamonds are a recent addition to the world of fine jewellery their future value is not yet known. The majority of diamond jewellery does not significantly appreciate in value over time, at least not in the wearer’s lifetime, and investment diamonds (of significant size and rarity) make up a very small proportion of diamonds traded. If someone is lucky enough to inherit your bespoke ring the value will be sentimental, because it’s from you.
Certification
All the white diamonds we source for your designs will be certified if they are above 0.30ct. Whether your diamond is lab grown or mined, it is graded in the same way and your diamond certificate will provide details of the Carat, Colour, Clarity and Cut from a reputable diamond grading laboratory. In addition to your certificate, it is now common practice for certified diamonds to be laser inscribed on the girdle with the certificate number and if lab grown it will also be inscribed with an ‘LG’ or ‘Laboratory Grown’ identifying the origin of your stone. (This inscription is really tiny and only visible through a 10x loupe.)
Insurance
Whether lab grown or mined, we always recommend insuring your diamond jewellery. Your insurance should cover the replacement value of your jewellery (as opposed to the resale value). As fine jewellery is made of precious metals and gemstones that fluctuate in market value it is always important to get your jewellery valued every couple of years, so that you are covered to the correct amount (your invoice should usually be suitable to cover you for the first two years). You should also be sure to keep your original diamond certificate in a secure place and make note of the report number allowing you to download an electronic copy of your certificate from the grading laboratory.
Care
Lab grown diamonds are real diamonds and should be looked after in the same way. Although diamonds are the hardest known mineral, making them an excellent choice for your engagement ring, this doesn’t mean they are invincible. All jewellery should be treated with love and care. We advise that you don’t wear your jewellery when doing anything where it could become knocked or damaged (rock climbing, DIY, washing up to name a few) as a knock in the wrong place could dislodge or chip a diamond. Read more about how to care for your jewellery here.


Lab Diamonds FAQs
How do you tell the difference between a Lab Grown and a Mined diamond?
In short, in everyday life, you can’t. A lab grown diamond will have the same brilliance, sparkle and fire of a mined diamond which is the same size and quality.
All Lab Grown diamonds above 0.30ct will be laser inscribed on the girdle with ‘LG’ or ‘Laboratory Grown’ to allow them to be identified when examined under magnification.
Diamond grading laboratories have specialist expertise and grading machines which enable them to tell Mined and Lab Grown diamonds apart. These techniques look for specific types of inclusions in Lab Grown diamonds and also differences in growth morphology of diamonds. For example Mined diamonds, HTHP and CVD diamonds grow into different shapes of diamond rough and identifying these directions of growth can tell a laboratory how the diamond was created.
Do Lab Diamonds test as real diamonds?
Diamond testers are designed to tell the difference between diamonds and diamond simulants, such as cubic zirconia. Lab Grown diamonds are made of pure carbon crystal, just as Mined diamonds are and so they will test positive when using a diamond tester. They are real diamonds!
Why are most Lab Grown diamonds round as opposed to fancy shapes like oval and princess?
Most diamonds available, Lab Grown or Mined, are round cut. A key reason for this is to meet demand; round brilliant cut diamonds are popular with consumers and jewellery designers because of their exceptional brilliance while their versatile shape suits lots of different designs. Another reason is because round diamonds optimise the carat weight available from a rough diamond. If you imagine two round brilliant diamonds, table to table, this is close to the shape of a rough diamond.
If you love the idea of a fancy shaped Lab Grown diamond – don’t worry, they are our there! Usually 1ct or larger, fancy shaped diamonds like Pear, Oval, Marquise do exist, let us know what you’re looking for and we’ll help you track down the right stone.
How much cheaper are Lab Grown diamonds compared to Mined diamonds?
Lab Grown diamonds are up to 30% less expensive than Mined diamonds. Though the technology, expertise and energy required to create a lab grown diamond is costly, it is still far more economical than mining. Once diamonds are grown or mined, the cost of cutting, polishing and assessing them is the same. This means that the price difference between Lab Grown and Mined diamonds is much less when dealing with small diamonds such as diamond melee, at which size the costs of cutting and polishing makes up a larger proportion of the diamond price.
What is the difference between a Lab Grown diamond and a Moissanite
They are different gemstones; diamonds, including Lab Grown diamonds are made from pure carbon whereas Moissanite is made from silicon carbide. Moissanite is a great gemstone in its own right, but it is also a well-liked alternative to diamond (or diamond simulant) due to its white colour and exceptional brilliance and durability. Natural Moissanite is incredibly rare and Lab Grown Moissanite is used in most Moissanite jewellery.
What is fluorescence in natural and Lab Grown diamonds
Fluorescence is characteristic which occurs in roughly 25% – 35% of diamonds, causing the stone to produce a colour reaction (usually blue) in response to ultraviolet light. Diamonds are made from 99.95% carbon and it’s the presence of elements such as nitrogen, aluminium and boron within the 0.05% that causes this phenomenon.
Fluorescence, particularly ‘strong fluorescence’ is generally avoided as it can make a diamond appear hazy. However in some instances, faint blue fluorescence can improve the appearance of a diamond with low colour, in making it look whiter in daylight.
There are noted differences in the intensity, colour and pattern of how lab grown and mined diamonds fluoresce, although there is overlap making this a difficult identifying characteristic.
*quote from Shanghai Diamond Exchange’s President, Qiang Lin
Live Loose Diamond Search
Find a diamond
Shape

Carat Weight
Cut
Colour
Clarity
Type
Select the perfect diamond shape for you. Round Brilliant diamonds are undoubtedly the most popular for their fire and sparkle but if you are looking for the variety and character of a fancy shape then see what else is available.
The size that suits your design, your taste and your budget. Carat weight refers to how heavy a diamond is. It is indicator of the size of the diamonds, however, you should refer to the measurements of the stone to get like for like comparisons.
The quality of a diamonds is arguably all about cut. An Excellent cut diamond will be fashioned so that it’s proportions, symmetry and polish result in superb brilliance, fire and sparkle.
White diamonds are graded by how colourless they are in appearance. D-F are Colourless, G-I are Near Colourless and K-Z are Tinted. The difference between each colour grading is slight and saving on colour can free up spending on the other Four Cs.
Clarity is an assessment of the number and position of visible inclusions in a diamond. For some shapes such as Emerald cut diamonds clarity is key, while for other more brilliant cuts, inclusions can become less noticeable.
Clarity is graded using the following abbreviations: IF/F meaning Internally flawless/ Flawless, VVS meaning Very Very Slightly included, VS meaning very slightly included, SI meaning Slightly Included and I is Included.
Polish grading is a recognition of how finely a diamond cut was finished. A diamonds Polish should enhance the cut by not interfering with light return.
Diamonds cuts are carefully calculated and planned for optimum light performance and beauty. The facets in a diamond should be perfectly aligned and shaped.
The depth of a diamond will impact the light performance and appearance of size. If a diamond is deep a lot of it’s carat weight will be ‘hidden’ beneath the stone where it can’t be enjoyed and the diamond will look smaller. Depth of a diamond also impacts light performance and a diamond that is too deep or too shallow will leak light.
The table needs to be well balanced to the proportions of the diamond. For a Round Brilliant diamond, the table should be around 54% – 57%
Fluorescence is the phenomenon in a diamond that causes a stone to produce a colour reaction (usually blue) in response to ultraviolet light. ‘Strong fluorescence’ is generally avoided as it can make a diamond appear hazy, however in some instances, faint blue fluorescence can improve the appearance of a diamond with low colour, in making it look whiter in daylight.
Our diamonds above 0.30ct will come with certification from an independent, reputable diamond grading laboratory. These include The American Gem Society (AGC), the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the International Gemological Institute (IGI)
Choose any special criteria for your diamond; Crafted by Infinity (CBI) for their impeccable cut quality, Mined diamonds from the Earth, Canadian diamonds with guaranteed provenance, or Lab Grown diamonds taking advantage of cutting edge technological developments.
Length-Width ratio of a fancy shaped diamond can be a matter what suits your personal taste and the ring design but it can also impact the beauty of the stone. Ideal ratios for different fancy shaped diamonds include Emerald diamonds = 1.34 – 1.43, Oval diamonds = 1.35 – 1.45, Pear diamonds = 1.47-1.65 and Marquise diamonds = 1.90 – 2.10
AS SEEN IN































